Emission of exhaust gases, especially SOx, NOx and atmospheric particles such as PM10 and PM2,5 emited by auxiliary engines of ships at berth affect directly and locally to air quality. Furthermore, CO2 emissions affect global warming.
Local impact estimation can be carried out using simulation techniques of pollutant diffusion; these techniques requiere high computional processing capacity. Local impact can be also estimated following the methodology presented and knowing the geographic position of each ship in port.
Below are presented the results of two case studies:
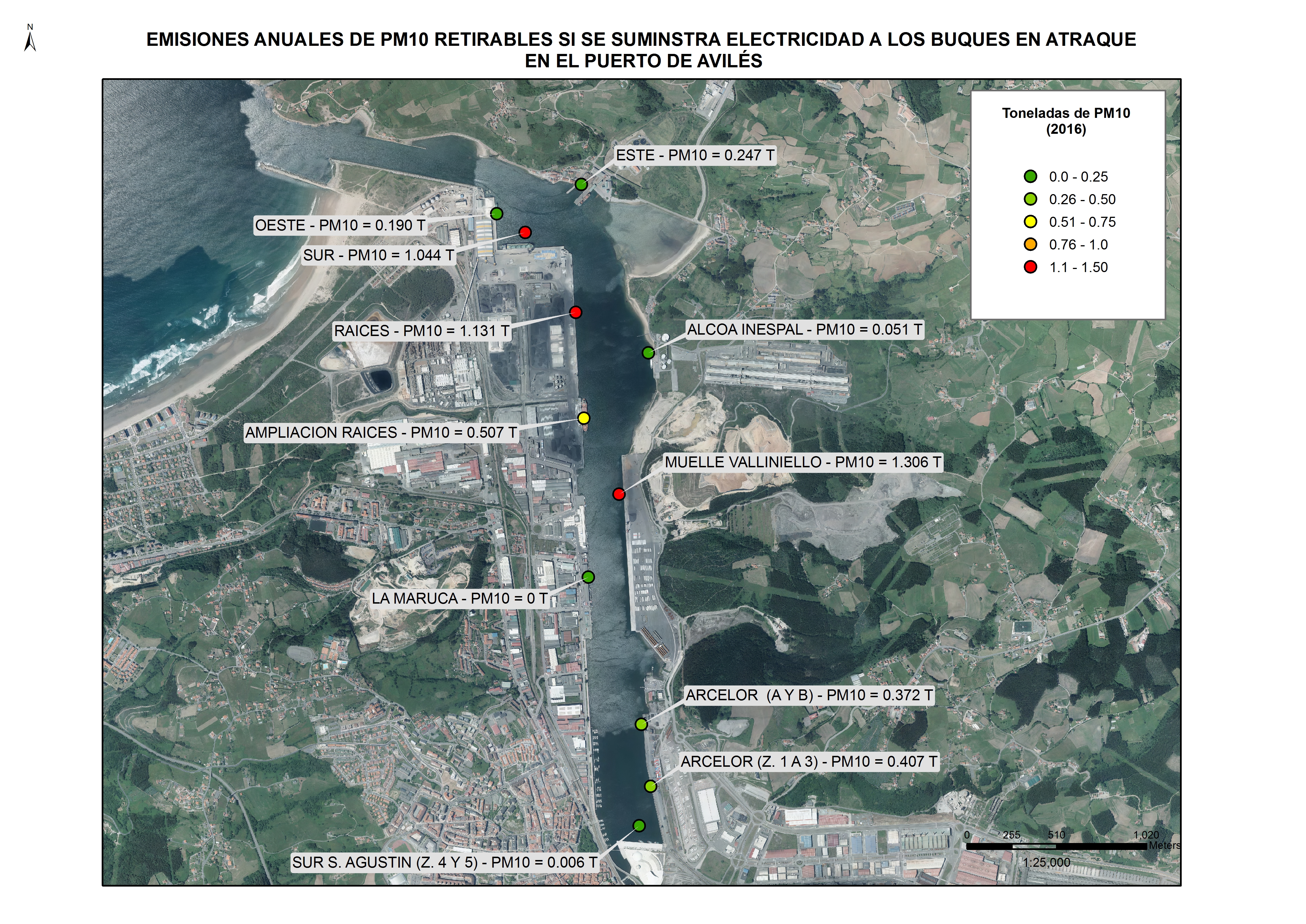
Case 1: PM10 annual tonnes estimating in Avilés Port in 2016:
Mooring points |
PM10 (T) |
|---|---|
ALCOA INESPAL |
0,051 |
AMPLIACIÓN RAÍCES |
0,507 |
ARCELOR (A Y B) |
0,372 |
ARCELOR (Z. 1 A 3) |
0,407 |
ESTE |
0,247 |
MUELLE VALLINIELLO |
1,306 |
OESTE |
0,190 |
RAÍCES |
1,131 |
SUR |
1,044 |
SUR AGUSTÍN (Z. 4 Y 5) |
0,006 |
LA MARUCA |
0,0 |
TOTAL |
5,26 |
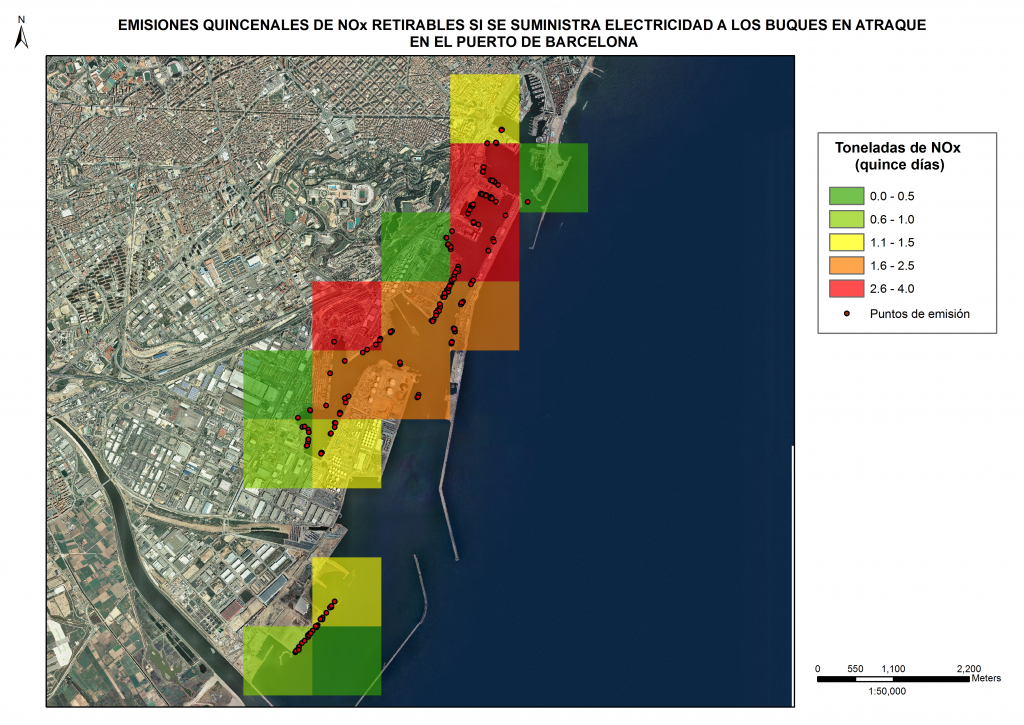
Case 2: NOx tonnes emitted to atmosphere by ships mooring in the port of Barcelona from the 1st to the 15th of January 2017.
1 to 15 of January 2017 |
Time at berth (h) |
Nº of ships berthing |
Auxiliary engines average power (kW) |
NOx Emissions (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Total |
4.255,5 |
265 |
651 |
23,4 |